
Research, Innovation & Development (RID)
Innovating through Research for a Sustainable Future

Innovating through Research for a Sustainable Future
In a world facing unprecedented challenges in the nexus of water, environment and climate, the RID Unit stands at the forefront of innovation, resilience, and progress. It embodies IWM’s unwavering commitment to pioneering excellence, where every project, every breakthrough, and every collaboration creates ripples of change far beyond borders. This ambitious unit is dedicated to pushing the boundaries of water-environment science, climate resilience, and integrated management through cutting-edge research and bold, solution-focused innovations.
IWM undertakes two types of research: one is sponsored research, meant for devising solutions to problems of national/international importance for its clients; and the other is for development of new tools and methods or for adaptation of some new technology or tools for future useful purposes, intended for providing better services to its clients in the long run. The second type of research may be undertaken either entirely by IWM's own resources or by resources drawn from partners and associates through collaboration/sub-contracts/joint ventures.
Over the years, the unit has successfully undertaken a wide range of completed and ongoing research initiatives, covering diverse areas such as flood risk assessment and forecasting, climate change and variability, drought analysis, integrated water resources assessment, water quality management, surface and groundwater hydrology, hydrogeology, irrigation and agricultural water management, river morphology, sediment transport, ecology and biodiversity, socio-economic and environmental studies, and sustainable and renewable energy solutions.
The RID Unit is charting a bold path toward a sustainable future, with its future priorities focused on climate-resilient water management, smart monitoring systems, groundwater sustainability and innovative solutions for enhancing the quality of wastewater. Driving advancements in ecosystem restoration, pollution mitigation, and climate modeling, the unit also embracing renewable energy integration, low-carbon innovations, and the transformative power of artificial intelligence from AI-powered early warning systems to its applications in allied fields.

Research and development activities, other than the aforesaid research projects, comprise variety of activities for generating knowledge, which are as follows:
These activities may be funded by IWM or by outside. However, these activities will be approved by the Executive Director.

Milestone Projects
This study investigated how large-scale tropical climate drivers—El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD), and Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) influence seasonal flooding patterns in Bangladesh, focusing on the period 1954–2024. Using flood-affected area (FAA) data, sea surface temperature (SST) anomalies, wind patterns, Principal Component Analysis (PCA), regression models, and Wavelet Coherence Analysis (WCA), the study provided new insights into flood variability, recurrence intervals, and predictive capabilities.
Key Findings of this study are as follows:
The study establishes that ENSO alone cannot fully explain Bangladesh’s flood dynamics. Instead, interactions among ENSO variants, IOD phases, and MJO activity jointly shape flood risks. Integrating real-time SST monitoring, ENSO variant classification, and PCA-based models into early warning systems can substantially improve seasonal flood forecasts and support climate-resilient water management in Bangladesh.
Climate Situation Summary Link for March-May of 2025: https://iwmbd.org/assets/uploads/iwm/service/Climate%20Situation%20Summary.pdf

The Goranchatbari Retention Pond (GRPA) in Dhaka serves as an important urban water body, yet its surrounding ecosystem has been suffering from severe pollution due to domestic sewage discharges, unregulated solid waste dumping, and urban runoff. To address this growing environmental concern, the Institute of Water Modelling (IWM) conducted an extensive technical study to assess the current state of the retention pond and connected khals, evaluate feasible water quality improvement technologies, and propose integrated, sustainable solutions for revitalizing the area.
The study began with a comprehensive field assessment, which included surveys, water sampling, and biodiversity analysis across multiple locations around the retention pond and its feeder khals, such as Rupnagar (Pallabi) Khal, Baunia Khal, Abdullahpur Khal, and Digun Khal. Twelve key water quality parameters—including pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), total dissolved solids (TDS), total suspended solids (TSS), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), ammonia, nitrate, total coliforms, and heavy metals—were analyzed seasonally and monthly. The study also assessed aquatic biodiversity to understand the ecological impacts of pollution. The plankton populations were relatively higher in the Abdullahpur Khal and retention pond, but were significantly lower in Rupnagar Khal, indicating pollution-induced ecosystem stress. Similarly, zooplankton diversity was reduced in polluted areas, while benthic species were found to be severely affected by plastic debris and organic waste accumulation. Overall, the findings revealed a substantial decline in biodiversity, emphasizing the urgent need for ecological restoration measures.
To identify suitable treatment technologies, the IWM team conducted a series of pilot experiments using physical, chemical, biological, and aeration-based interventions:
Filter-based treatments using gravel, brick chips, and gravel-sand combinations showed moderate improvement in TSS, BOD, and COD levels. Gravel-sand filters performed best, removing up to 33% TSS and 15% COD, but their low hydraulic permeability limits scalability. However, none of the filters effectively reduced coliform contamination due to bacterial growth on filter media.
Aeration treatments proved far more effective. Among the tested technologies, the disc diffuser system performed best, significantly improving DO levels and achieving up to 42% TSS reduction, 84% BOD improvement, 53% COD reduction, and 41% coliform reduction. Paddle aerators and nano-bubble tubes also showed promising results, especially when combined with overnight settling, but were less effective for coliform control compared to disc diffusers.
Chemical dosing experiments using alum and lime demonstrated moderate success. At higher concentrations, both chemicals improved DO levels and reduced suspended solids, but lower dosages caused inconsistent results, sometimes even increasing COD and coliform counts due to incomplete settling.
Biological treatment via constructed wetlands showed significant potential for long-term, eco-friendly solutions. Among the five tested plant species, Canna Indica and Phragmytes adapted well to polluted conditions and exhibited healthy growth, while Water Lily, Lotus, and Water Snowflake failed to survive in the experimental setup. Constructed wetlands using suitable plants offer a sustainable approach for improving water quality while restoring ecological balance.
The study concludes that domestic wastewater pollution is the primary driver of poor water quality in the Goranchatbari retention pond and its surrounding khals. Physical treatments alone are insufficient to meet environmental standards. Instead, the results highlight the need for hybrid treatment systems that combine disc diffuser aerating fountains with constructed wetlands. This integrated approach not only improves dissolved oxygen levels and reduces organic pollutants, but also restores aquatic biodiversity over time.
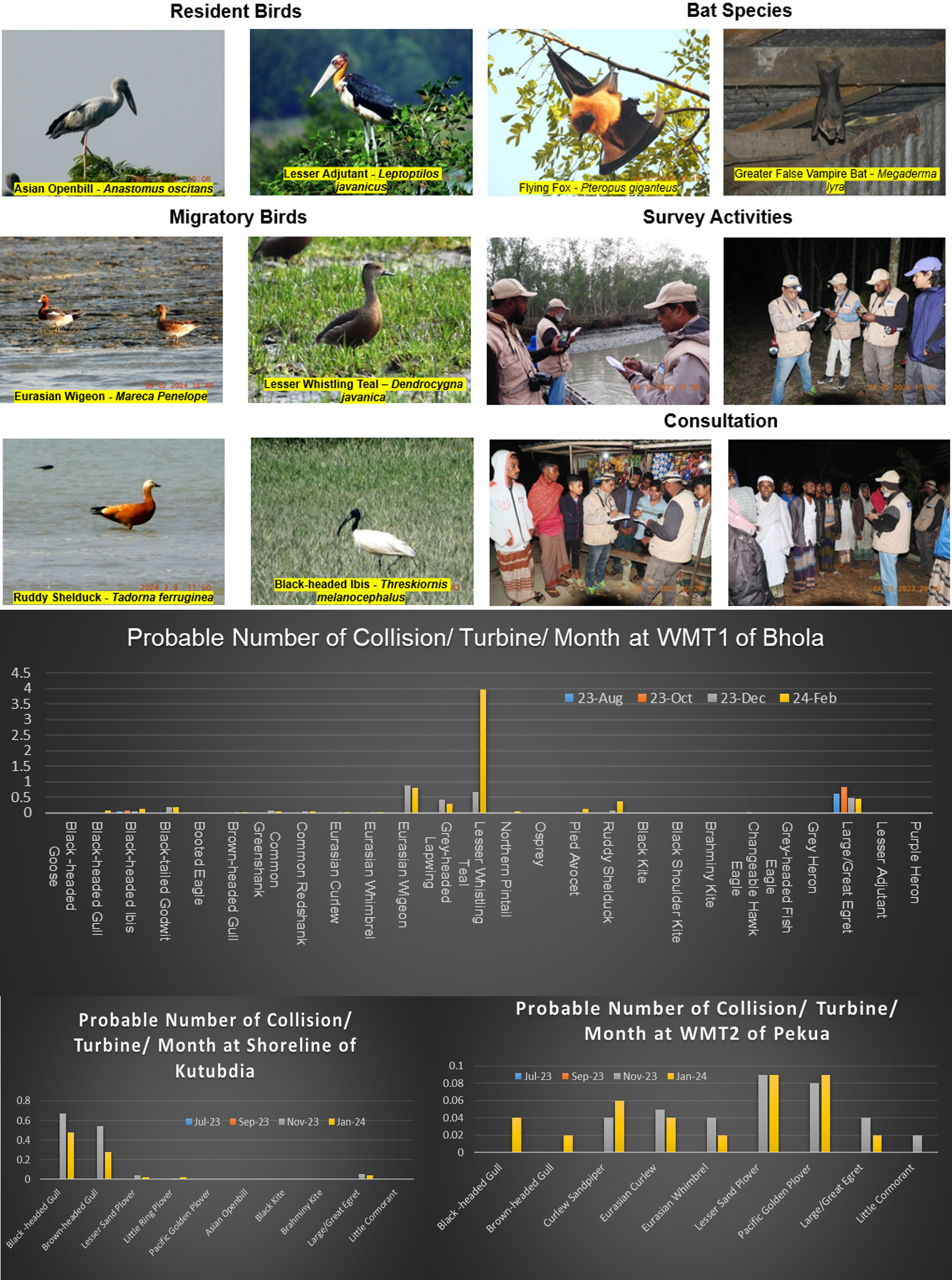
The study was designed to evaluate the ecological implications of developing wind energy at two coastal sites in Bangladesh, Bhola and Kutubdia. Conducted over a fifteen-month period, the research focused specifically on surveying bird and bat populations, their habitats, flight activities, breeding and migratory patterns, and identifying species that could be vulnerable to collisions with wind turbines. The study responded to Bangladesh’s ambition to expand renewable energy under the Renewable Energy Policy, but it also recognized that such development must be balanced with biodiversity conservation.
At Bhola, three wind monitoring stations were surrounded by habitats that supported a rich variety of bird and bat species. The survey revealed significant bat populations, particularly Flying Foxes and Greater False Vampire Bats, whose flight altitudes often coincided with the projected height of turbine blades. Bird observations were equally revealing: more than seventy species were recorded, spanning resident, breeding, and migratory groups. Bhola’s coastal lines and wetlands proved especially important as staging grounds for migratory birds traveling along international flyways. These findings established that parts of Bhola, especially around WMT-1 and WMT-3, are ecologically sensitive and pose a considerable collision risk if turbines are erected there.
Kutubdia and Pekua, on the other hand, supported somewhat fewer species, though still noteworthy for both bats and birds. Here, the same two bat species were observed as in Bhola, with flight heights again overlapping turbine rotor zones. Bird surveys documented nearly sixty species, including migratory waterbirds making use of coastal mudflats and aquatic habitats. While risks were present, these sites showed slightly lower bird density and migratory traffic than Bhola, suggesting they may offer more feasible locations for turbine installation provided mitigation measures are enforced.
The collision risk models estimated that turbine operation at these sensitive sites could lead to significant mortality rates over time, potentially threatening local populations of resident species and disrupting international migratory routes. Even if the absolute number of collisions is low, the impact on rare or vulnerable species could be severe due to their smaller population sizes. The study recommended a suite of mitigation strategies, such as avoiding turbine placement in high-density habitats, especially Bhola’s WMT-1 and WMT-3 areas; creating buffer zones around wetlands and coastal forests; adjusting turbine numbers and heights; and applying operational curtailment during peak bird migration and bat activity. Additional measures included habitat restoration, the use of deterrent technologies, and establishing long-term monitoring programs.
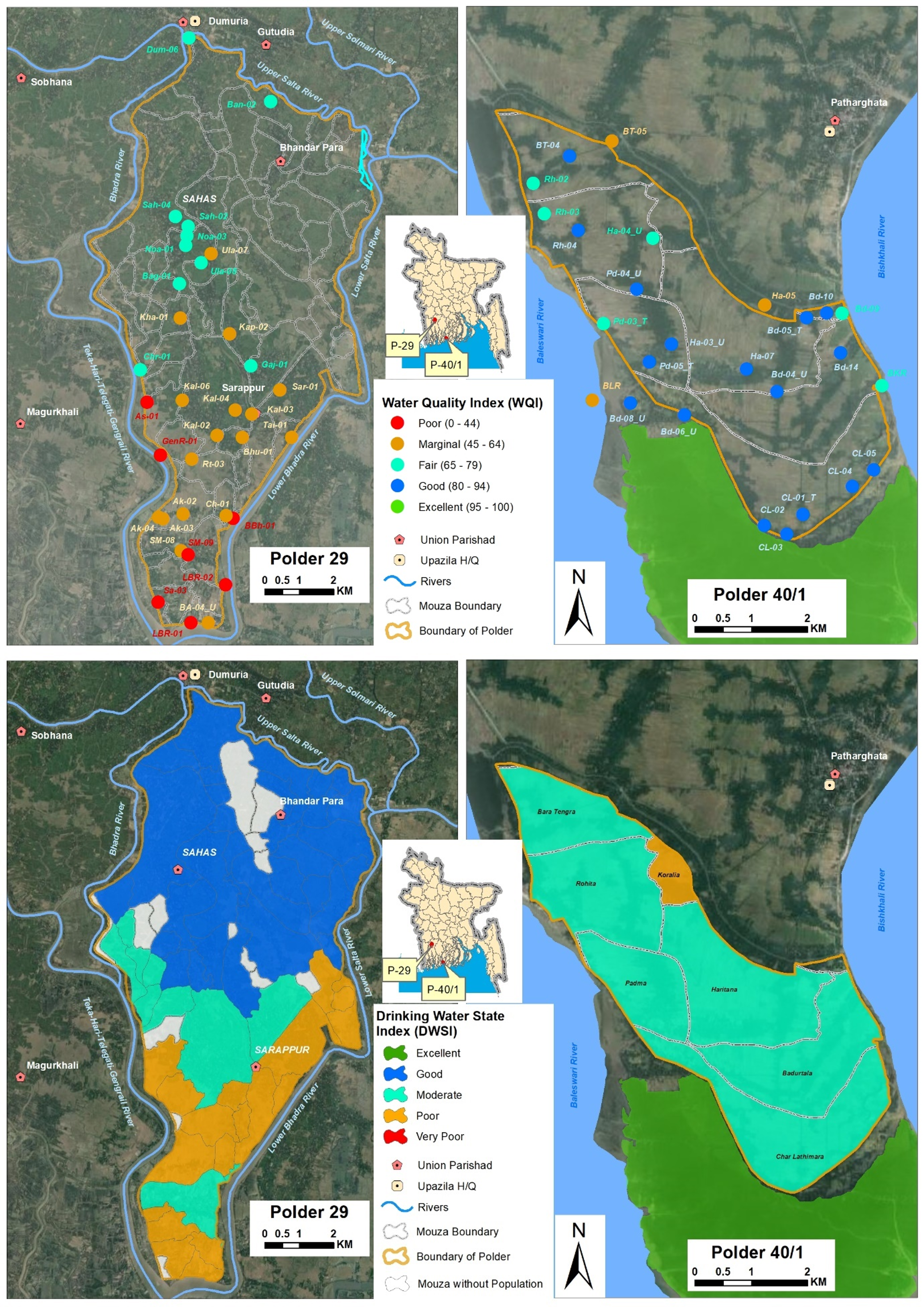
This study was carried out under the framework of long-term monitoring and research on the country’s coastal polders. The central objective was to examine the availability, quality, and sustainability of drinking water resources in two representative coastal zones—Polder 29, which is relatively less saline and located further inland, and Polder 40/1, which is directly exposed to the sea and faces high salinity.
To achieve this, the researchers combined both field-based and secondary data. Household surveys, focus group discussions, key informant interviews, geophysical resistivity surveys, hydrogeochemical testing, and exploratory drilling were conducted to understand the present water sources, the extent of crisis, and future risks. Alongside, hydrological and meteorological data from relevant agencies were used to model water recharge, groundwater salinity, and demand projections. To interpret the water quality and accessibility, two indices were applied: the Water Quality Index (WQI) and a newly developed Drinking Water State Index (DWSI), which allowed the assessment of conditions at the mouza level.
The quality of available water was found to be a serious concern. In Polder 29, several parameters, including salinity, total dissolved solids, calcium, bicarbonates, and iron, often exceeded drinking water standards. Groundwater recharge in this polder, though sufficient to meet present demand, is under severe threat as salinity is projected to increase drastically by 2050, with almost all groundwater sources expected to become unsuitable. In Polder 40/1, surface water quality is somewhat better, yet pH and iron concentrations remain problematic. Health problems such as diarrhea, dysentery, and skin diseases were commonly reported in both areas as consequences of unsafe water use.
When the overall water situation was assessed through the DWSI, neither of the polders showed excellent conditions. In Polder 29, some areas were categorized as “good,” but a large number fell under “moderate” or “poor.” In Polder 40/1, the majority of mouzas were found in “moderate” condition, with one mouza classified as “poor.” These results underscore the precarious state of safe drinking water in both zones.
The research focused on developing a two-stage pre-monsoon flash flood forecasting system for the north-east haor region of Bangladesh, an area highly vulnerable to sudden floods during April–May. These flash floods, triggered by heavy convective rainfall, regularly damage Boro rice crops, the region’s main livelihood and a major contributor to national food security.
The forecasting system combined two approaches:
Probabilistic rainfall prediction (1-month lead time): Developed using the Climate Predictability Tool (CPT) to support policy-level planning.
Deterministic rainfall forecast (7-day lead time): Developed using the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF-ARW) model to provide more precise short-range warnings.
Additional components included testing different cumulus physics schemes for thunderstorm simulation and validating satellite rainfall products against observed data.
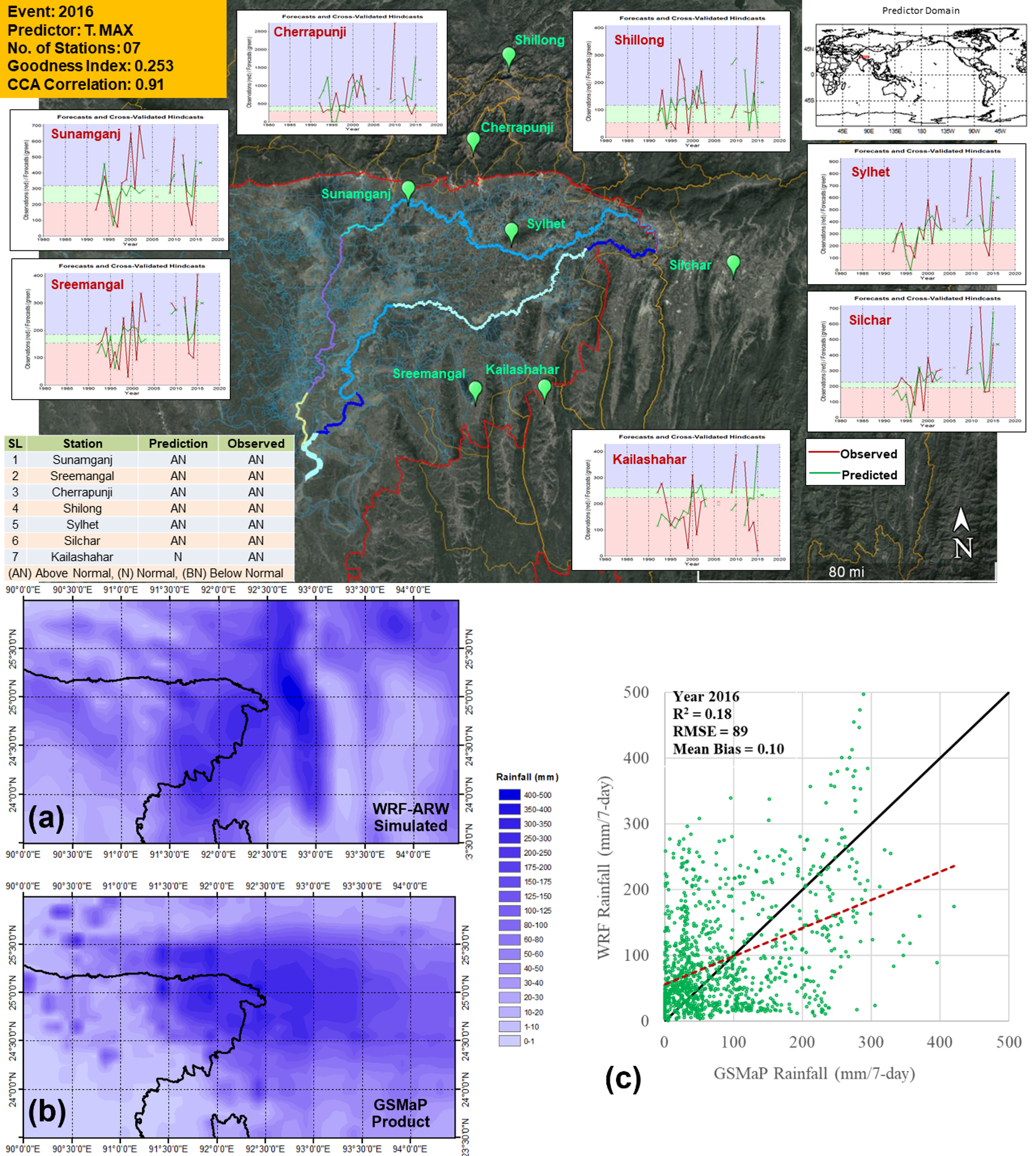
The analysis showed that only a few large-scale climate variables namely maximum temperature, sea surface temperature, and geopotential height at certain atmospheric levels—had strong statistical connections with observed rainfall in the region. These predictors were found to be more reliable when used individually rather than in combination, suggesting that single-parameter correlations were stronger for forecasting rainfall. The CPT-based forecasts proved to be effective for years such as 2016 and 2017, both of which saw major flash flood events, while in other years like 2018, 2020, and 2021 the predictions tended to overestimate rainfall. This highlighted both the potential and the limitations of the probabilistic method.
On the short-range side, the WRF-ARW model was tested with different cumulus physics schemes to determine which would best capture thunderstorm activity. The Kain-Fritsch scheme, when paired with the Global Forecast System (GFS) dataset, provided the most consistent results. Using this setup, the model was able to simulate the defining features of severe thunderstorms, including sharp drops in mean sea level pressure, strong multi-level wind flows, vertical wind shear, high vorticity, and intense convective energy. These conditions aligned well with observed storm dynamics in 2016 and 2017, where the model’s rainfall simulations closely resembled actual events. However, the model’s performance faltered in later years; it overestimated rainfall in 2020 and underestimated it in 2021, revealing the continuing challenge of accurately simulating convective rainfall in complex environments.
The study also evaluated several satellite rainfall products to see how well they could complement the forecasts. Among these, GSMaP consistently outperformed others like CHIRPS and TRMM/GPM-IMERG, especially for capturing heavy rainfall events above 50 millimeters per day. GSMaP’s better alignment with observed data made it a valuable validation tool and a promising resource for operational use.
Recent riverbank erosion at Naria Upazila of Shariatpur district is a national concern due to its diverse impacts on the country's economy and insecure entity of bank dwellers. This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of dredging works and river training works (RTW) through mathematical modelling for river bank protection at Naria, Shariatpur district. To observe the morphological changes near Naria along the right bank of Padma River, a 55 km length of Padma reach from Dohar to 30 km downstream of Mawa was selected for the model domain. The bankline near Naria was updated with the bank line of post-monsoon of 2018. Four different options were developed based on dredging alignment and RTW works. Dredging along the right side of existing char (Option 1) is the most effective one showing good performance in comparison to the other two proposed dredging alignments. And series of spurs along the bend at the immediate u/s of Naria (Option 4) is an individual case for placing spurs along the bend, which certainly lessens the erosion but incorporating rigid structure in the middle of the river like Padma may result in aggressive consequences in the long-term river morphology.

The study focused on evaluating and developing sediment transport predictors suitable for the Brahmaputra–Jamuna River in Bangladesh, where heavy sediment loads strongly influence channel dynamics, erosion, deposition, and floodplain stability. Using long-term suspended sediment data from BWDB, IWM, and earlier survey projects, the researchers compared six widely used sediment transport equations—Engelund-Hansen (1967), Van Rijn (1984), Ackers-White (1973), Yang (1973), Bagnold (1966), and Hossain (1985)—against hundreds of measured datasets at key locations such as Bahadurabad and Bangabandhu Bridge.
The analysis showed that the Engelund-Hansen, Van Rijn, and Hossain equations gave the best match with observed data. Among these, Hossain’s formula is particularly significant as it was developed using field data from Bangladesh’s major rivers, while the other two were derived mainly from laboratory flume experiments. The success of these equations is partly explained by the Jamuna’s median sediment size (0.16–0.23 mm), which falls within the applicable range of these models.
Beyond testing existing formulas, the researchers also attempted to create a new sediment predictor tailored to the Jamuna River, using recent suspended sediment data collected by IWM. They developed a dimensionless relationship between sediment transport and shear stress. However, a limitation was that the data were collected near hydraulic interventions (e.g., Bangabandhu Bridge, Sirajganj Hard Point), meaning local conditions may have influenced results.
To further validate the findings, the Engelund-Hansen, Van Rijn, and the newly developed IWM predictor were incorporated into a two-dimensional morphological model (MIKE 21C). The model covered a 40 km reach around the Bangabandhu Bridge. Simulations of flow, scour, and channel formation were compared with field measurements and satellite imagery. Results showed that the IWM predictor produced promising outcomes: the simulated channel planform closely resembled observed post-monsoon 2016 conditions, scour patterns near the bridge matched measured data, and sediment transport values fell within acceptable ranges.
Finally, when the accuracy of different predictors was tested against observed sediment discharge, the IWM equation showed the greatest improvement in reducing bias, followed by Engelund-Hansen and Van Rijn.
In conclusion, the study demonstrated that while Engelund-Hansen and Van Rijn remain useful, the newly developed IWM sediment transport equation holds strong promise for the Jamuna River, offering better alignment with observed data.

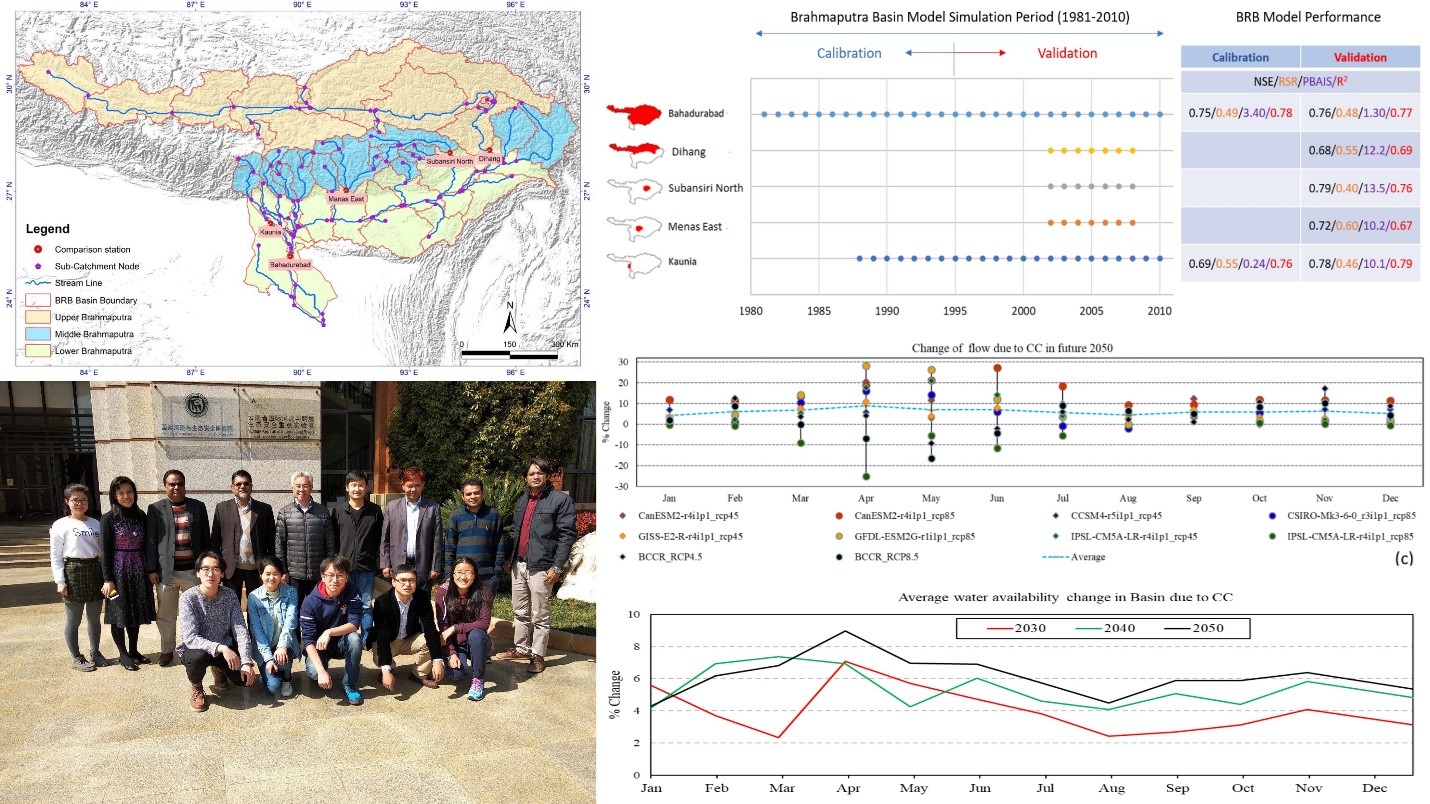
A joint research project was conducted with Yunnan University, China on “Water Resources Vulnerability and Security Assessment of Yarlung Tsangpo – Brahmaputra Transboundary River Basin”. The Brahmaputra, the world’s 4th largest river by annual flow, is the main river of the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna system, carrying the highest flow and sediment to the Bay of Bengal across China, India, Bhutan, and Bangladesh. It supports about 130 million people, whose livelihoods and regional development depend on the basin, which is highly vulnerable to climate change impacts. This study is an effort to assess impact of change on water availability of Brahmaputra River basin. In this study, Brahmaputra Basin (BRB) Model has been calibrated at 5 different locations in different sub-catchments. Finally, the calibrated model is applied to estimate future streamflow using 8 general circulation model (GCM) output under two representative concentration pathways (RCP). It is observed that out of ten scenarios analyzed almost nine cases show a similar trend, i.e. increase of flow due to climate change. Most of climate scenarios show significant change of flow in basin in April, May and June. However, a very strong change in peak flow is projected, which may lead to a devastating flood in future.
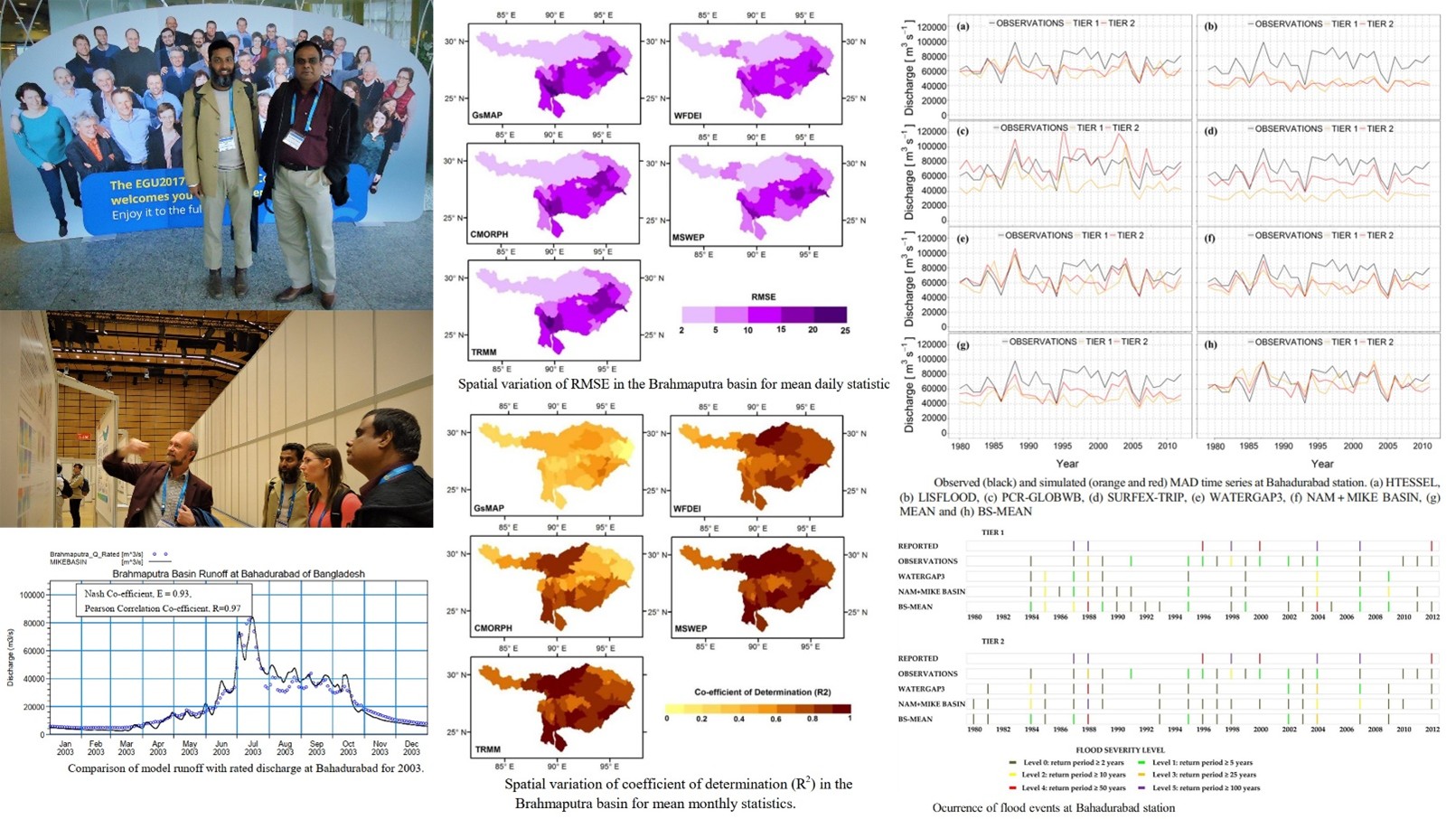
This project has received funding from the European Union’s Seventh Programme for research, technological development and demonstration. Work package 6 of the eartH2Observe project consisted of a number of case-studies to evaluate the applicability of the Earth Observation (EO) data from WP3 and the Water Resources Reanalysis (WRR) data from WP5 for water management at national or river basin levels. Moreover, this WP also provided feedback to WP3 on the quality and use of the EO datasets, and WP5 on the added value of the WRR for hydrological modelling purposes. The testing of and feedback on the EO and WRR data helped to improve the eartH2Observe data products for water resources analysis and water management at the river basin or national levels.
Core Team Members
Email: mrh@iwmbd.org
Mobile: 01841930015
Email: asf@iwmbd.org
Mobile: 01629659540
Email: kna@iwmbd.org
Mobile: 01738436186
Email: ntt@iwmbd.org
Mobile:
Email: frz@iwmbd.org
Mobile:
Email: szh@iwmbd.org
Mobile: 01725991405