
Flood and River Basin Management (FRM)
Innovative Solutions for Sustainable Flood Resilience and River Basin Stewardship

Innovative Solutions for Sustainable Flood Resilience and River Basin Stewardship
The Flood and River Basin Management Division of IWM extends its expertise beyond Bangladesh to countries like Nepal, India, Tajikistan, and others, with the mission of providing sustainable solutions for managing flood risks and river systems. Their vision is to enhance regional resilience through integrated water resource management, focusing on reducing the impacts of floods, river erosion, and sedimentation. By leveraging advanced modeling tools, real-time data systems, and stakeholder collaboration, the division aims to promote climate-adaptive strategies and foster transboundary cooperation for the long-term management of river basins and water resources in these regions.







Our Milestone Projects
Detailed Narrative Description of Project:
The assignment is being carried out under a credit program of World Bank. The main objective of the assignment is to develop a sustainable and operational Mathematical Modelling Center (MMC) in Bihar, India. Thus, along with development of several mathematical models, resource development is being continued through both formal and on the job training. The consultant team is also giving management support to FMISC as and when required. Professionals from FMISC are participating in different layers of development of mathematical models. The models were supposed to be updated or developed using primary data. But due to unavailability of primary data in time, the models are being updated or developed mostly based on secondary data available in public domain and very limited quantity of primary data. Under the project, the existing Bagmati-Adhwara River Flood Forecasting Model has been updated which is operational at FMISC. A Regional Network Model comprising entire area of Bihar has also been developed which has finally been transferred into a Regional Flood Forecasting Model. The Regional Flood Forecasting Model of Bihar has been experimentally operated in 2019 to generate flood forecast with 3-days lead time at a total of 40 Nos. of stations located on different rivers following in Bihar.
Detailed Description of Actual Services:
Updating Existing Flood Forecasting Model of Bagmati-Adhwara River Basin: this is the 1st Task of the project under which the existing model has been updated with available cross-sections along with incorporation of some important tributaries. The existing model has also been extended up to a reasonable extent in downstream. The model is being operated based on real time rainfall, water level and discharge data made available from FMISC and public domain.
Development of Regional Network Model: A Regional Network Model comprising entire territory of Bihar, India has been developed based on MIKE 11 (NAM & HD) software of DHI, Denmark. The Regional Network Model includes a total of 128 Nos. of sub-catchments delineated based on satellite-based DEM of JAXA/SRTM and field features made available from FMISC as well as public domain (Google Earth). The model comprises 13 significant river basins of Bihar. The Regional Network Model has been calibrated for hydrological event of 2016, and subsequently validation has been checked for 2015, 2017 and 2018.
Development of Regional Flood Forecasting Model: A Regional Flood Forecasting Model of Bihar has been developed taking the Network Model with some extended areas in upstream basins in Nepal and few other states of India. The model is developed based on four modules of MIKE 11: NAM, HD, FF and DA of DHI, Denmark. The Regional Flood Forecasting Model uses real time rainfall, water level, discharge data made available from FMISC and public domain. In addition to real time gauge data, rainfall forecast with 3-days lead time received from IMD is used. The model produces flood forecast in a total of 40 Nos. of gauge stations maintained by CWC and WRD. Flood forecast are produced as hydrographs and Bulletin.

Detailed Narrative Description of Project:
The Northeast Region (NE) of Bangladesh comprises 17.5% of the total area of Bangladesh. There are altogether 373 Haors distributed in the districts of Sylhet, Sunamganj, Moulvibazar, Habiganj, Netrokona, Kishoreganj and Brahmanbaria. The Haor areas are frequently affected by the flash flood, generated in the steep upland catchments adjacent to the region in India. Flash flood usually occurs during pre-monsoon and early flash floods during the months of April-May damage the main crop Boro rice nearly or just before the harvesting. The early flash flood of April 2004, 2016 and 2017 triggered severe flash floods over northeastern parts of the country causing severe damage to food crops, housing and infrastructure, including bridges and roads. Flood Forecasting and Warning Services (FFWS) in Bangladesh is the mandate of Bangladesh Water Development Board (BWDB) under Ministry of Water Resources. Flood Forecasting and Warning Center (FFWC) of BWDB is carrying out this responsibility on behalf of BWDB.
The overall objective of the project is to develop a dedicated early warning system for flash flood in the NE region of Bangladesh for saving boro rice.
The other objectives are
Increase number of flash flood forecast stations up to 25 locations;
Produce diversified forecast outputs and make FFEWS operational;
Dedicated flash flood forecasting web-page of FFWC;
Capacity building of FFWC professionals in flash flood forecasting.
The major tasks that have been carried out under this project are:
Established real-time data collection of 29 nos. rainfall and 39 nos. real-time water level gauges including two automatic sensor based gauges installed under this project;
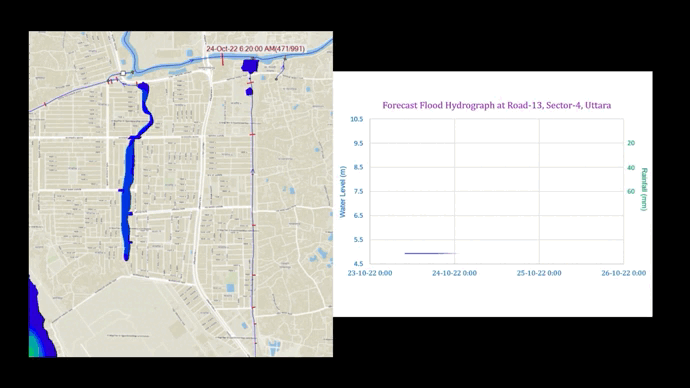
Update of flash flood forecast model, generate and disseminate forecast warning and evaluation of performance for 2017, 2018 and 2019 flash flood event (fig 2);
Increase forecast stations up to 25 nos. and expand forecast coverage area in B.Baria, Sherpur, Netrokona, Kishoreganj along with Sylhet, Sunamganj, Habiganj and Moulvibazar in the North-Eastern Bangladesh;
Fixation and implementation of pre-monsoon danger level at 25 nos. forecast stations and
Generation of flash flood forecast outputs (hydrograph, summary bulletin, observed and forecast bulletin, embankment based forecast, quantitative precipitation forecast, mobile apps based forecast etc.).
One can access the website using FFWC website (www.ffwc.gov.bd) and then clicking on flash flood forecast page.

Detail Narrative Description of Project:
The study has been conducted to update the existing flood forecasting system of FFWC for effective flood management in the country. The existing Rainfall Runoff model has been updated by redistribution of catchment contribution (Northeast Region) as well as incorporating additional 30 more rainfall stations. The hydrodynamic model has been updated through adding 463 nos. new cross-sections (in 32 rivers) made available from Hydrology, BWDB, updating alignment of major rivers, incorporating one new river (Dudkumar River) and optimizing parameters (mainly resistance parameter: Manning’s M). Seven flood forecast stations have been added under this updating program. From now on FFWC will be able to provide flood forecast at a total of 61 stations instead of existing 54 stations. About 650 km of additional flood protection embankment has been added in the flood map preparation system. In the updated system, flood inundation feature has improved in several areas like Pabna Irrigation and Rural Development Project (PIRDP), Chalan Beel, and Gaibandha area. An alternative of existing FLOOD WATCH, a new tool named “FLOOD VIEW” has been developed using C-Sharp and Python programming language.
Major activities performed in this project:
Collection and review of reports, relevant documents, existing flood forecasting activities, past attempts for increasing forecast stations etc.
Increase forecast stations by reviewing field requirements and consultation with FFWC.
Updating of the boundaries of the FFWC super model.
Update FFWC Super Model (Hydraulic) using information from flash flood forecast model.
Improve the flood maps quality by applying updated information.
Provide support to update website with increased forecast stations
.png)
Detail Narrative Description of Project:
Development and Upgradation of the Existing Flood Forecast Model: The first task under the study is the expansion of flood forecasting model covering whole Bangladesh. The existing flood forecasting model has been transferred to MIKE+ which is the new version of MIKE software. After that the Rainfall Runoff model has been expanded by incorporating of 90 new sub catchments. The 1D Hydrodynamic model has also been transferred to MIKE+ and has been expanded covering whole Bangladesh incorporating 168 new rivers. The Model has been calibrated for hydrological year 2021 and validated for 2019,2020 and 2023.
Major activities performed in this project:
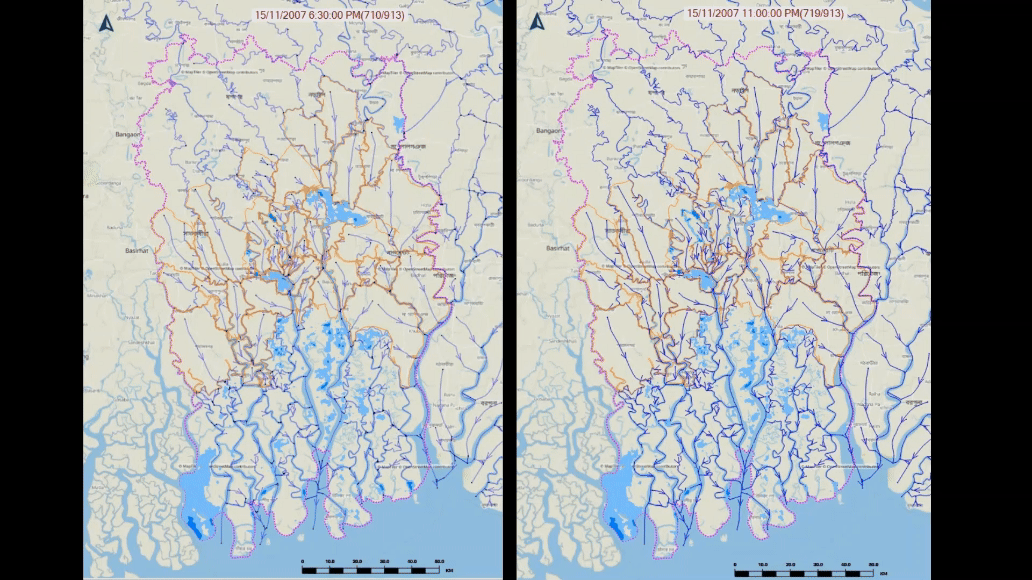
Development Flood Inundation Model: Under this study second task is upgradation of existing flood inundation model covering whole country and development of 1D-2D couple model for coastal areas of Bangladesh. The existing inundation model has been expanded to provide flood inundation forecast for whole Bangladesh using MIKE + 1D model and ArcGIS environment. For dynamic flood inundation 1D-2D couple model has been developed for coastal areas of Bangladesh which is around 47,201 sq. km and located in Southwest, South-central, Southeast and Eastern Hill regions covering 19 districts. The 1D-2D Couple Model has been calibrated based on available Sentinel-1 satellite images in Google Earth Engine. The model has the capacity to simulate flood inundation occurring in the coastal area during extreme weather conditions.
Upgradation of the Existing Decision Support System: The third task under the study is upgradation of the existing decision support system based on FLOOD WATCH to MIKE OPERATIONS. DHI has launched MIKE OPERATIONS as a replacement for MIKE FLOOD WATCH. So, the existing decision support system has been updated into MIKE OPERATIONS platform. This software platform allows integrating modelling tools for forecasting purposes, such as rainfall-runoff model and river and reservoir routing models. The model integration, with so-called adapters, allows smooth and automated data input into and model results from the models. The data repository of this software platform is a PostgreSQL database.

Detailed Narrative Description of Project:
The Northeast Region of Bangladesh has special natural features called the Haors which are large bowl-shaped flood plain depressions. These haors are enriched with various aquatic biodiversity’s along with about 140 species of fish. These haors are frequently affected by flash flood, generated in the steep upland catchments adjacent to the border region of India. Sudden intrusion of flash flood recurrently destroys agricultural production of about 0.33 million ha. More than 28% of the total population in the area lives below the Lower Poverty Line.
For this reason, since inception, a substantial number of water management projects have been implemented by the Bangladesh Water Development Board in the area. The board is now implementing a program in the area under a credit programme of Japan’s Official Development Assistance. Nippon Koei Co. Ltd. Japan, Joint Venture with BETS Consulting Services Ltd. Bangladesh and Center for Natural Resources Studies, Bangladesh is providing overall consultancy services for implementation of the project. Institute of Water Modelling is providing sub-consultancy services for mathematical modeling and topographic survey under a contract agreement with Nippon Koei Co. Ltd. Japan. Major assignment of the program includes construction /rehabilitation and reconstruction of flood management infrastructure in 29 haors of greater northeast region.
Detailed Description of Actual Services Provided by your Staff:
The project includes the flood and drainage study in the Haor area through utilizing mathematical techniques and topographic survey. The aim of the consultancy services is to support the detailed design and implementation with respect to analyzing data/information to generate a series of flash flood scenarios leading to confinement effect due to the implementation of flood management infrastructure of the targeted 29 haors. The consultancy services comprise of mathematical model study and primary and secondary data collection through field survey. Specific tasks of the project are:
Topographic survey of 29 nos. haor sub-projects;
Hydrometric and topographic data collection from secondary sources and field campaign for mathematical modelling;
Development and simulation of Hydrological and Hydraulic models and scenario simulation;
Preparation of detail planning for 29 nos. haor sub-projects to provide pre-monsoon flood protection and improve post-monsoon drainage;
Determination of parameters for detail design of proposed structures;
Provide flood inundation statistics for different scenario;
Preparation of topographic and detail planning maps of 29 nos. haor sub-projects;
Preparation of site plan for proposed structures.

Detailed Narrative Description of Project:
The Hindu Kush-Himalayan (HKH) region contains the largest amount of snow and ice found outside the Polar Regions and is the source of 10 of the largest rivers in Asia. The Brahmaputra river is one of the major rivers of HKH region comprising a basin area of around 520,600km2. The river is shared among 4 countries, China, India, Bhutan and Bangladesh. Under the HICAP programme, a contract agreement was signed between ICIMOD and IWM to study the Brahmaputra river basin. The study commenced in February 2012 and to be continued up to August 2013. The overall goal of the study is to improve our understanding and knowledgebase on water resources in the Brahmaputra basin. The study mainly focuses present availability and demand of water resources in the basin area along with the adaptation options under various climate change scenarios. The study is being carried out based on the secondary information and data mostly publicly available domain, published books and web-pages and also data available with IWM and ICIMOD.
Description of activities carried out so far:
Assessment of the current knowledgebase including historic water resources availability and demand trends, and water resources development strategies in the basin area;
Development of hydrological model for the basin area using MIKE Basin software of DHI and its application for various scenarios
Assessment of water availability and demand corresponding to baseline and future climate scenarios at basin and reasonable sub-basin scales;
Improve our understanding of the partitioning of runoff contribution from different natural sources (snow glacier, rainfall, groundwater, etc.);
Identified most vulnerable sub-basins/ catchments to hydrological impacts of climate change; and
Identified, assessed and prioritized suitable adaptation options according to its effectiveness in terms of reducing vulnerability to the threats of hydrological impacts of climate change.

Our Core Team


Email: ral@iwmbd.org
Mobile: 01841-930050
Phone: 880-2-55087611-4